Fuel injection system of motorcycle Ducati ST2 (1997-2003)
See this section in russian language
Description of fuel injection-ignition system
The use of an electronic fuel injection-ignition system for the internal combustion engine optimises engine performance and creates higher specific power, as well as lower specific consumption and a reduction in the amount of unburnt elements in the...
The use of an electronic fuel injection-ignition system for the internal combustion engine optimises engine performance and creates higher specific power, as well as lower specific consumption and a reduction in the amount of unburnt elements in the...
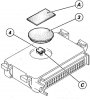
Electronic control unit
The injection-ignition system control unit is e micro-processor digital electronic control unit; it controls the parameters relating to the fuel supply for end ignition of the engine: the quantity of fuel supplied to each cylinder in sequence (1-2)...
The injection-ignition system control unit is e micro-processor digital electronic control unit; it controls the parameters relating to the fuel supply for end ignition of the engine: the quantity of fuel supplied to each cylinder in sequence (1-2)...
Changing the Eprom
The Eprom contains the engine control mapping. This important element can be changed as follows: Remove the adhesive plate (A) applied during testing by the Manufacturer. At reassembly, apply plate (B) code number 433.1.180.1A available from the...
The Eprom contains the engine control mapping. This important element can be changed as follows: Remove the adhesive plate (A) applied during testing by the Manufacturer. At reassembly, apply plate (B) code number 433.1.180.1A available from the...
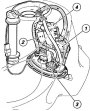
Fuel circuit in injectors
The fuel is injected by the electro-injectors in the intake manifold of each cylinder, upstream of the intake valve. The circuit consists of a pump (1), a filter (2), a pressure regulator (3) and a degasser (4) connected to the lower flange of the...
The fuel is injected by the electro-injectors in the intake manifold of each cylinder, upstream of the intake valve. The circuit consists of a pump (1), a filter (2), a pressure regulator (3) and a degasser (4) connected to the lower flange of the...
Electric fuel pump
The electric pump is volumetric and has rotating lobes, with the motor immersed in the fuel. It is a brush motor energised by permanent magnets. The pump has a non-return valve which prevents emptying of the fuel circuit when the pump is not...
The electric pump is volumetric and has rotating lobes, with the motor immersed in the fuel. It is a brush motor energised by permanent magnets. The pump has a non-return valve which prevents emptying of the fuel circuit when the pump is not...
Electro-injector for control the quantity of fuel
The injector is used to control the quantity of fuel fed into the engine. The injector consists of a body (1) and a needle (2) connected to the magnetic armature (3). The needle is pressed on the seal seat by a helical spring (4), whose load is set...
The injector is used to control the quantity of fuel fed into the engine. The injector consists of a body (1) and a needle (2) connected to the magnetic armature (3). The needle is pressed on the seal seat by a helical spring (4), whose load is set...
Fuel pressure regulator
The regulator is required to keep the pressure stage constant on the injectors. It is a diaphragm differential regulator set at 3 Bar during assembly. The fuel under pressure, coming from the pump, creates a thrust on the rotor (1 and 2) countered...
The regulator is required to keep the pressure stage constant on the injectors. It is a diaphragm differential regulator set at 3 Bar during assembly. The fuel under pressure, coming from the pump, creates a thrust on the rotor (1 and 2) countered...
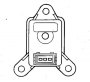
Absolute pressure sensor
The absolute pressure sensor is powered by the electronic unit and supplies information about the absolute air pressure in a neutral area of the motorbike. The pressure sensor sends an absolute air pressure signal for correction in accordance with...
The absolute pressure sensor is powered by the electronic unit and supplies information about the absolute air pressure in a neutral area of the motorbike. The pressure sensor sends an absolute air pressure signal for correction in accordance with...
Air temperature and coolant temperature sensors
The sensor (1) measures the external air temperature; the electric signal created is sent to the electronic unit and is used for correction in accordance with the air temperature. The sensor (2) measures the temperature of the coolant in the engine....
The sensor (1) measures the external air temperature; the electric signal created is sent to the electronic unit and is used for correction in accordance with the air temperature. The sensor (2) measures the temperature of the coolant in the engine....
Power coil and module
An inductive discharge ignition system is used. The power coils and modules (built into the unit) are controlled by the I.A.W. control unit which calculates the ignition advance. The power module also guarantees a coil load with constant energy,...
An inductive discharge ignition system is used. The power coils and modules (built into the unit) are controlled by the I.A.W. control unit which calculates the ignition advance. The power module also guarantees a coil load with constant energy,...
Throttle position potentiometer
The potentiometer is powered by the electronic unit to which it sends a signal which identifies the position of the throttle. This information is used by the unit as a main parameter for calculating the dose of fuel and the ignition advance. Note....
The potentiometer is powered by the electronic unit to which it sends a signal which identifies the position of the throttle. This information is used by the unit as a main parameter for calculating the dose of fuel and the ignition advance. Note....
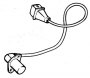
The pick up sensor
The pick up used is inductive: it is facing the timing gear and can read the 46 teeth and the discontinuity of 2 teeth. The signals coming from the pick up are used by the unit to acquire the engine RPM and as a timing reference. Note. To check...
The pick up used is inductive: it is facing the timing gear and can read the 46 teeth and the discontinuity of 2 teeth. The signals coming from the pick up are used by the unit to acquire the engine RPM and as a timing reference. Note. To check...
Functioning stages
Normal functioning If the engine has the correct temperature, the I.A.W. unit calculates the timings, the injection time and the advance, by comparing the stored map values, in accordance with the RPM and throttle angle. The quantity of fuel set in...
Normal functioning If the engine has the correct temperature, the I.A.W. unit calculates the timings, the injection time and the advance, by comparing the stored map values, in accordance with the RPM and throttle angle. The quantity of fuel set in...
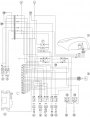
Ignition and injection system diagram
Wiring diagram legend 1) Tank with fuel pump and fuel level sensor 2) Electronic control unit 3) Diagnosis tester socket 4) Throttle rotation potentiometer 5) Water temperature sensor 6) Engine sensor 7) Fuses for injection relay 8) Air temperature...
Wiring diagram legend 1) Tank with fuel pump and fuel level sensor 2) Electronic control unit 3) Diagnosis tester socket 4) Throttle rotation potentiometer 5) Water temperature sensor 6) Engine sensor 7) Fuses for injection relay 8) Air temperature...
Similar subsections of other motorcycle models
Fuel injection motorcycle Harley-Davidson V-Rod (2002-2006)
Fuel injection motorcycle Yamaha YZF-R1 (2009-2014, 7 generation)
- Information for owner
- Technical characteristics
- Maintenance
- Engine and systems
- Engine repair
- Fuel and exhaust system
- Fuel injection
- Cooling and lube system
- Transmission
- Running gear and frame
- Frame and hinged elements
- Wheels and tires
- Brake system
- Front suspension and handlebar
- Rear suspension
- Electric equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Starting and charging system