Warning: Batteries generate explosive hydrogen gas and contain electrolyte which is made of poisonous and highly caustic sulfuric acid.
Therefore, always follow these preventive measures:
- Wear protective eye gear when handling or working near batteries.
- Charge batteries in a well-ventilated area
- Keep batteries away from fire, sparks or open flames (e.g., welding equipment, lighted cigarettes).
- DO NOT SMOKE when charging or handling batteries.
- Keep batteries and electrolyte out of reach of children.
- Avoid bodily contact with electrolyte as it can cause severe burns or permanent eye injury.
- First aid in case of bodily contact: external
- Skin — Wash with water.
- Eyes — Flush with water for 15 minutes and get immediate medical attention.
- Internal
- Drink large quantities of water or milk followed with milk of magnesia, beaten egg or vegetable oil. Get immediate medical attention.
Notice: This is a sealed battery. Never remove the sealing caps because the balance between cells will not be maintained and battery performance will deteriorate.
Charging time, charging amperage and charging voltage for an VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery are different from those of conventional batteries. The VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery should be charged as explained in the charging method illustrations. If the battery is overcharged, the electrolyte level will drop considerably. Therefore, take special care when charging the battery.
Since VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) batteries are sealed, it is not possible to check the charge state of the battery by measuring the specific gravity of the electrolyte. Therefore, the charge of the battery has to be checked by measuring the voltage at the battery terminals.
1. Remove:
- Rider seat
- Battery cover
Refer to "General chassis".
2. Disconnect:
- Battery leads (from the battery terminals)
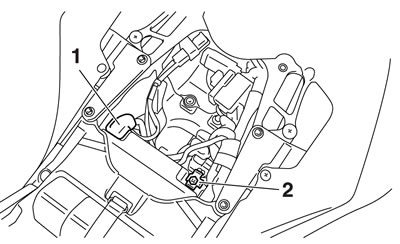
Notice: First, disconnect the battery negative lead "1", and then battery positive lead "2".
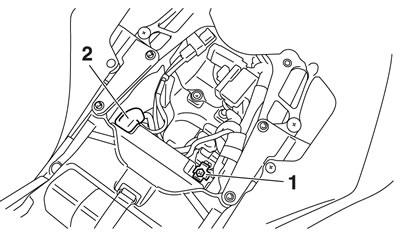
Remove:
- Battery
4. Check:
- Battery charge
a. Connect a pocket tester to the battery terminals.
Positive tester probe Positive battery terminal
Negative tester probe Negative battery terminal
The charge state of an VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery can be checked by measuring its open-circuit voltage (i.e., the voltage when the positive battery terminal is disconnected).
No charging is necessary when the open-circuit voltage equals or exceeds 12.4 V.
b. Check the charge of the battery, as shown in the charts and the following example.
Example:
- Open-circuit voltage = 12.0 V
- Charging time = 6.5 hours
- Charge of the battery = 20-30%
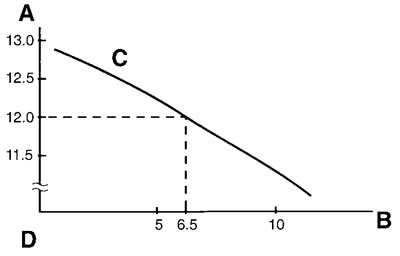
A. Open-circuit voltage (V); B. Charging time (hours); C. Relationship between the open-circuit voltage and the charging time at 20°C (68°F); D. These values vary with the temperature, the condition of the battery plates, and the electrolyte level.
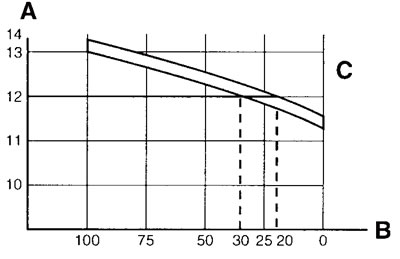
A. Open-circuit voltage (V); B. Charging condition of the battery (%); C. Ambient temperature 20°C (68°F)
5. Charge:
- Battery (refer to the appropriate charging method illustration)
Warning: Do not quick charge a battery.
Notice:
- Never remove the VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery sealing caps.
- Do not use a high-rate battery charger since it forces a high-amperage current into the battery quickly and can cause battery overheating and battery plate damage.
- If it is impossible to regulate the charging current on the battery charger, be careful not to overcharge the battery.
- When charging a battery, be sure to remove it from the vehicle. (If charging has to be done with the battery mounted on the vehicle, disconnect the battery negative lead from the battery terminal.)
- To reduce the chance of sparks, do not plug in the battery charger until the battery charger leads are connected to the battery.
- Before removing the battery charger lead clips from the battery terminals, be sure to turn off the battery charger.
- Make sure the battery charger lead clips are in full contact with the battery terminal and that they are not shorted. A corroded battery charger lead clip may generate heat in the contact area and a weak clip spring may cause sparks.
- If the battery becomes hot to the touch at any time during the charging process, disconnect the battery charger and let the battery cool before reconnecting it. Hot batteries can explode!
- As shown in the following illustration, the open-circuit voltage of an VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery stabilizes about 30 minutes after charging has been completed. Therefore, wait 30 minutes after charging is completed before measuring the open-circuit voltage.
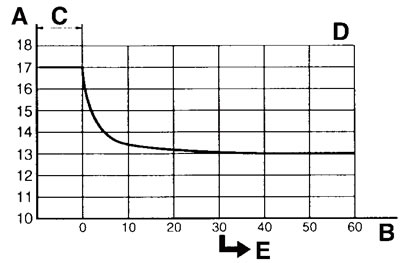
A. Open-circuit voltage (V); B. Time (minutes); C. Charging; D. Ambient temperature 20°C (68°F); E. Check the open-circuit voltage.
Charging method using a variable-current (voltage) charger
a. Measure the open-circuit voltage prior to charging.
Voltage should be measured 30 minutes after the engine is stopped.
b. Connect a charged and ammeter to the battery and start charging.
Set the charging voltage at 16-17 V. If the setting is lower, charging will be insufficient. If too high, the battery will be over-charged.
c. Make sure that the current is higher than the standard charging current written on the battery.
If the current is lower than the standard charging current written on the battery, set the charging voltage adjust dial at 20-24 V and monitor the amperage for 3-5 minutes to check the battery.
- Reach the standard charging current: Battery is good.
- Does not reach the standard charging current: Replace the battery.
d. Adjust the voltage so that the current is at the standard charging level.
e. Set the time according to the charging time suitable for the open-circuit voltage.
f. If charging requires more than 5 hours, it is advisable to check the charging current after a lapse of 5 hours. If there is any change in the amperage, readjust the voltage to obtain the standard charging current.
g. Measure the battery open-circuit voltage after leaving the battery unused for more than 30 minutes.
- 12.4 V or more — Charging is complete.
- 12.3 V or less — Recharging is required.
- Under 12.0 V — Replace the battery.
Charging method using a constant voltage charger
a. Measure the open-circuit voltage prior to charging.
Voltage should be measured 30 minutes after the engine is stopped.
b. Connect a charger and ammeter to the battery and start charging.
c. Make sure that the current is higher than the standard charging current written on the battery.
If the current is lower than the standard charging current written on the battery, This type of battery charger cannot charge the VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery. A variable voltage charger is recommended.
d. Charge the battery until the battery's charging voltage is 15 V.
Set the charging time at 20 hours (maximum).
e. Measure the battery open-circuit voltage after leaving the battery unused for more than 30 minutes.
- 12.4 V or more — Charging is complete.
- 12.3 V or less — Recharging is required.
- Under 12.0 V — Replace the battery.
6. Install:
- Battery
7. Connect:
- Battery leads (to the battery terminals)
Notice: First, connect the battery positive lead "1", and then the battery negative lead "2".
8. Check:
- Battery terminals
Dirt → Clean with a wire brush.
Loose connection → Connect properly.
9. Lubricate:
- Battery terminals
- Recommended lubricant
- Dielectric grease
10. Install:
- Battery cover
- Rider seat
Refer to "General chassis".
