
Bearings
Before proceeding to check wheel dimensions, check the wear of the wheel hub and sprocket flange bearings. Clean and degrease the bearings in situ, and then check bearing wear by hand.
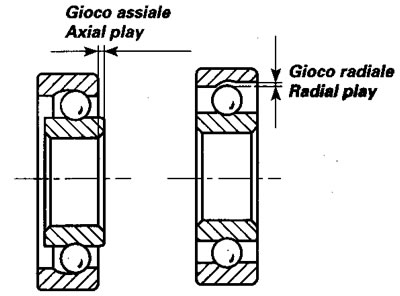
Turn the inner ring and push it In and out to check for the amount of radial and axial wear. Excessive bearing wear will cause vibrations and will make the bike unstable. Badly worn bearing must therefore be changed.
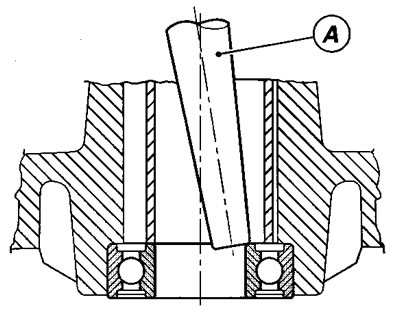
Using a hammer and a pin (A) knock the inner bearing ring and drive the bearing out.
Change the position of the pin continuously to drive the bearing out of the housing as straight as possible.
Caution! Do not refit bearings once they have been removed.
Before you fit new bearings, check that the seat is clean and free from scoring and damage.
Grease the bearing seat and then push the bearing into the seat.
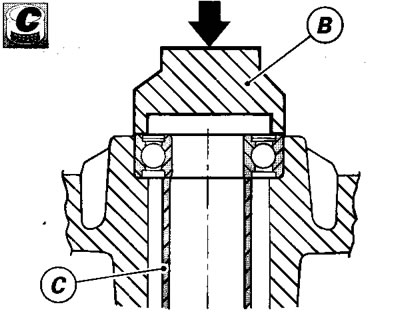
Using a tubular drift (B) which only exerts pressure on the outer bearing ring, drive the bearing fully into its seat.
Ensure that you fit the spacer (C) between the two wheel hub bearings.
Note. Wheels must be rebalanced after repair, maintenance and overhaul operations.
Wheel spindle
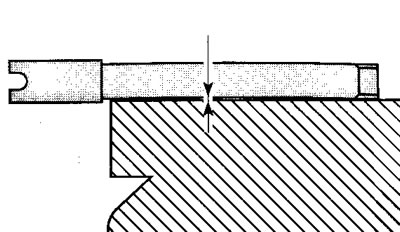
Check the distortion of the wheel spindle. Roll the spindle on a reference surface and check the maximum distortion using a feeler gauge.
Distortion limit on 100 mm/ 3.937 in.: 0.2 mm/0.0078 in.
 |  |
Rims
After you have checked the bearings, check the rims as follows: О Inspect the rim for cracks, scoring and deformation; change damaged rims.
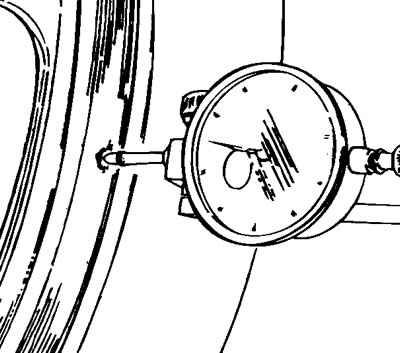
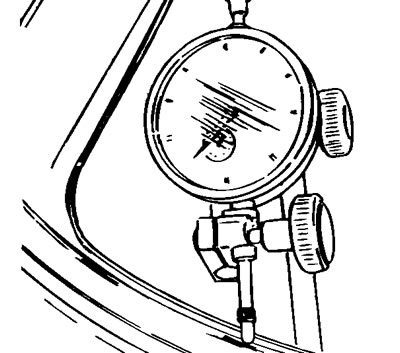
Insert the wheel spindle in the wheel and mount the wheel on two fixed reference blocks.
Using a dial gauge, measure the rim run-out and out-of-round. Standard values:
Run out: 0.5 mm/0.0196 in.
Out-of round: 0.8 mm/0.0314 in.
Service limit: 2 mm/0.0787 in.
If the values measure are not within these limits, change the rim.
 |  |
