Note: Insufficient compression pressure will result in a loss of performance.
1. Check: valve clearance
Out of specification → Adjust. Refer to "Adjusting the valve clearance".
2. Start the engine, warm it up for several minutes, and then turn it off.
3. Disconnect: spark plug cap
4. Remove: spark plug
Caution! Before removing the spark plugs, use compressed air to blow away any dirt accumulated in the spark plug wells to prevent it from falling into the cylinders.
5. Install: compression gauge (1)
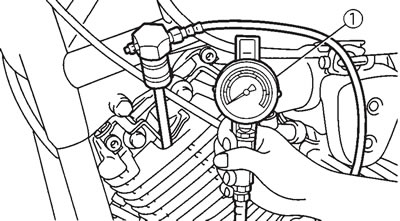
- Compression gauge set: 90890-03081
6. Measure: compression pressure
- Above the maximum pressure Inspect the cylinder head, valve surfaces, and piston crown for carbon deposits.
- Below the minimum pressure Squirt a few drops of oil into the affected cylinder and measure again.
Refer to the following table.
| Compression pressure (with oil applied in the cylinder) | |
| Reading | Diagnosis |
| Higher than without oil | Piston wear or damage → Repair. |
| Same as without oil | Piston ring(-s), valves, cylinder head gasket or piston possibly defective → Repair. |
Compression pressure (at sea level):
- Standard: 1000 kPa (10 kg/cm², 10 bar)
- Minimum: 900 kPa (9 kg/cm², 9 bar)
- Maximum: 1100 kPa (11 kg/cm², 11 bar)
a. Turn the main switch to "ON".
b. With the throttle wide open, crank the engine until the reading on the compression gauge stabilized.
Warning! To prevent sparking, ground all spark plug leads before cranking the engine.
Note: The difference in compression pressure between cylinders should not exceed 100 kPa (1 kg/cm², 1 bar).
7. Install: spark plug: 20 Nm (2.0 m·kg)
8. Connect: spark plug cap
