Periodic service of motorcycle Aprilia RS125 3 (RS-series, 1999-2005)
See this section in russian language
Regular service intervals chart
Introduction To keep your vehicle in top performance conditions, Aprilia strongly recommends to respect the routine maintenance schedule for the different parts of the vehicle. This section describes the routine maintenance operations for vehicle...
Introduction To keep your vehicle in top performance conditions, Aprilia strongly recommends to respect the routine maintenance schedule for the different parts of the vehicle. This section describes the routine maintenance operations for vehicle...
Points to be lubricated
A good lubrication ensures vehicle smooth operation and durability. Note. Before lubrication, clean all parts from any rust deposits, grease, dirt or dust. The points to be lubricated are specified in the "LUBRICATING CHART". ■ = Grease ▲ = Oil...
A good lubrication ensures vehicle smooth operation and durability. Note. Before lubrication, clean all parts from any rust deposits, grease, dirt or dust. The points to be lubricated are specified in the "LUBRICATING CHART". ■ = Grease ▲ = Oil...
Multifunction computer
Key: 13. LAP push button 14. MODE push button ( M ) 15. LOCK push button ( L ) 16. START push button ( S ) 17. Upper display 18. Lower display Functions description Turn ignition switch (7) to "". Press the push button M repeatedly so as to make the...
Key: 13. LAP push button 14. MODE push button ( M ) 15. LOCK push button ( L ) 16. START push button ( S ) 17. Upper display 18. Lower display Functions description Turn ignition switch (7) to "". Press the push button M repeatedly so as to make the...
Nut, bolt, screw tightening
Check after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Check all fastening parts with accuracy. Mainly check all safety-related components and, in particular: Handlebar-to-upper plate fastener; Front brake control...
Check after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Check all fastening parts with accuracy. Mainly check all safety-related components and, in particular: Handlebar-to-upper plate fastener; Front brake control...
Tightening torques of fastening elements
Check and, if necessary, tighten after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and after every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Warning! The fastening elements specified in the table must be tightened to the specified torque value using a torque wrench and, where...
Check and, if necessary, tighten after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and after every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Warning! The fastening elements specified in the table must be tightened to the specified torque value using a torque wrench and, where...
Battery — precautions
Carefully read 1.2.1. Two different types of battery are available on the market: battery needing to be maintained with plugs; maintenance-free battery without plugs needing no electrolyte level check and topping up. After the first 1000 km (621 mi)...
Carefully read 1.2.1. Two different types of battery are available on the market: battery needing to be maintained with plugs; maintenance-free battery without plugs needing no electrolyte level check and topping up. After the first 1000 km (621 mi)...
Checking and cleaning the terminals of battery
Carefully read 2.4.1. Make sure that the ignition switch is in position "". Raise the fuel tank, see 2.9.1. Make sure that the cable terminals (1) and the battery terminals (2) are: in good conditions (and not corroded or covered with deposits);...
Carefully read 2.4.1. Make sure that the ignition switch is in position "". Raise the fuel tank, see 2.9.1. Make sure that the cable terminals (1) and the battery terminals (2) are: in good conditions (and not corroded or covered with deposits);...
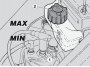
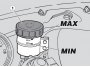
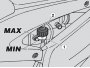
Checking the battery electrolyte level
Carefully read 2.4.1. Lift the fuel tank, see 2.9.1. Keep the vehicle in vertical position, with the two wheels resting on the ground. Make sure that the fluid level is included between the "MIN" and "MAX" marks, etched on the battery side. If this...
Carefully read 2.4.1. Lift the fuel tank, see 2.9.1. Keep the vehicle in vertical position, with the two wheels resting on the ground. Make sure that the fluid level is included between the "MIN" and "MAX" marks, etched on the battery side. If this...
Recharging the battery
Carefully read 2.4.1. Note. If the battery is almost fully flat, when the starting button "" is pressed, the starting relay will issue a vibrating noise. Do not remove the battery plugs: without plugs the battery may be damaged. Remove the battery,...
Carefully read 2.4.1. Note. If the battery is almost fully flat, when the starting button "" is pressed, the starting relay will issue a vibrating noise. Do not remove the battery plugs: without plugs the battery may be damaged. Remove the battery,...
Long inactivity of the battery
Carefully read 2.4.1. Warning! If the vehicle remains unused for more than twenty days, disconnect the 20A fuses, in order to avoid the deterioration of the battery caused by the current consumption due to the multifunction computer. The removal of...
Carefully read 2.4.1. Warning! If the vehicle remains unused for more than twenty days, disconnect the 20A fuses, in order to avoid the deterioration of the battery caused by the current consumption due to the multifunction computer. The removal of...
Checking electrical parts
Carefully read 1.2.1. Check after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Position the vehicle on the stand. Make sure that all lighting devices are working properly. Check for headlight correct aiming, 8.15.1. Make...
Carefully read 1.2.1. Check after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Position the vehicle on the stand. Make sure that all lighting devices are working properly. Check for headlight correct aiming, 8.15.1. Make...
Spark plugs maintenance
Spark plug tightening torque: 20 Nm (2.0 kg·m). Check the spark plug after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then after 4000 km (2485 mi), change it every 8000 km (4970 mi). Periodically remove the spark plug and clean it carefully, removing carbon...
Spark plug tightening torque: 20 Nm (2.0 kg·m). Check the spark plug after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then after 4000 km (2485 mi), change it every 8000 km (4970 mi). Periodically remove the spark plug and clean it carefully, removing carbon...
Air cleaner maintenance
Check the air cleaner every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months, change it every 8000 km (4970 mi) or more frequently if the vehicle is used on dusty or wet roads. It is possible to clean the air cleaner partially after using the vehicle on this kind of...
Check the air cleaner every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months, change it every 8000 km (4970 mi) or more frequently if the vehicle is used on dusty or wet roads. It is possible to clean the air cleaner partially after using the vehicle on this kind of...
Fuel lines, oil pipes and tubes
Fuel Check fuel lines every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Change them every four years. Warning! In case of wear, cracking or other damage, change the fuel lines. For further information, see section 4 ( FUEL SYSTEM ). Mixer oil Carefully read...
Fuel Check fuel lines every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months. Change them every four years. Warning! In case of wear, cracking or other damage, change the fuel lines. For further information, see section 4 ( FUEL SYSTEM ). Mixer oil Carefully read...
Lifting the fuel tank
Carefully read 1.2.1. Tank front screw (1): 7 Nm (0.7 kg·m). Turn the fuel cock to the "OFF" position. Remove the seat, see 7.1.1. Unscrew and remove the screw (1). Keep the bushing. Take the tank rod from the tool kit. Lift the front part of the...
Carefully read 1.2.1. Tank front screw (1): 7 Nm (0.7 kg·m). Turn the fuel cock to the "OFF" position. Remove the seat, see 7.1.1. Unscrew and remove the screw (1). Keep the bushing. Take the tank rod from the tool kit. Lift the front part of the...
Checking and topping up the coolant level
Carefully read 1.2.1 and 1.3.1. Check the coolant level before starting and change it every two years. Warning! Check the coolant level and top up the expansion reservoir with cold engine. Stop the engine and wait until it has cooled down. Note....
Carefully read 1.2.1 and 1.3.1. Check the coolant level before starting and change it every two years. Warning! Check the coolant level and top up the expansion reservoir with cold engine. Stop the engine and wait until it has cooled down. Note....
Adjusting the clutch
Clutch shall be adjusted when the engine is coming to a stop or when the vehicle tends to move with the clutch lever pulled and a gear is engaged or, if the clutch is "slipping", the deceleration will be delayed if compared to the engine rpm. Minor...
Clutch shall be adjusted when the engine is coming to a stop or when the vehicle tends to move with the clutch lever pulled and a gear is engaged or, if the clutch is "slipping", the deceleration will be delayed if compared to the engine rpm. Minor...
Checking and topping up the front brake fluid level
Carefully read 1.2.1 and 1.3.1. Check the brake fluid after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months, change it every year. Warning! In case of excessive stroke of the brake lever, excessive elasticity, or air...
Carefully read 1.2.1 and 1.3.1. Check the brake fluid after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months, change it every year. Warning! In case of excessive stroke of the brake lever, excessive elasticity, or air...
Changing the brake fluid
Carefully read 1.2.1. and 1.3.1. Brake fluid must be changed every year. Note. These operations apply to both front and rear brakes. Warning! When using the fluid, take care not to spill it on the plastic and painted parts, since it damages them....
Carefully read 1.2.1. and 1.3.1. Brake fluid must be changed every year. Note. These operations apply to both front and rear brakes. Warning! When using the fluid, take care not to spill it on the plastic and painted parts, since it damages them....
Checking the brake pad wear
Carefully read 1.2.1 , 1.3.1 and 2.1.2. NOTE. The following information refer to a single braking system, but are valid for both. Check the brake pad wear after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and successively every 2000 km (1242 mi). The wear of the...
Carefully read 1.2.1 , 1.3.1 and 2.1.2. NOTE. The following information refer to a single braking system, but are valid for both. Check the brake pad wear after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and successively every 2000 km (1242 mi). The wear of the...
Checking and topping up the rear brake fluid
Carefully read 1.2.1 and see 1.3.1. Check the brake fluid after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months, change it every year. Warning! In case of excessive stroke of the brake lever, excessive elasticity, or air...
Carefully read 1.2.1 and see 1.3.1. Check the brake fluid after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and then every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months, change it every year. Warning! In case of excessive stroke of the brake lever, excessive elasticity, or air...
Bleeding the braking systems
Carefully read 1.2.1 and 1.3.1. For maintenance operations, see 2.1.2. The air, if any, present inside the hydraulic circuit will serve as "pad" by absorbing most of the pressure coming from the brake master cylinder and thus reducing the calipers...
Carefully read 1.2.1 and 1.3.1. For maintenance operations, see 2.1.2. The air, if any, present inside the hydraulic circuit will serve as "pad" by absorbing most of the pressure coming from the brake master cylinder and thus reducing the calipers...
Adjusting the rear brake control lever
The brake pedal is placed in an ergonomic position during vehicle assembly. If necessary, the brake pedal height can be adjusted to fit your riding position: Loosen the check nut (1). Fully loosen the brake adjuster (2). Tighten the lock nut (3) on...
The brake pedal is placed in an ergonomic position during vehicle assembly. If necessary, the brake pedal height can be adjusted to fit your riding position: Loosen the check nut (1). Fully loosen the brake adjuster (2). Tighten the lock nut (3) on...
Adjusting the gearbox lever
The gearbox lever can be adjusted using the transmission rod (1). Proceed as follows: Loosen the nuts (2, 3). Rotate the transmission rod and adjust the gearbox lever height. Tighten the nuts (2, 3). The gearbox lever pin is constantly greased...
The gearbox lever can be adjusted using the transmission rod (1). Proceed as follows: Loosen the nuts (2, 3). Rotate the transmission rod and adjust the gearbox lever height. Tighten the nuts (2, 3). The gearbox lever pin is constantly greased...
Checking for throttle proper operation
Inspect after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months afterwards. Caution! Throttle operation may be impaired when the throttle cables are damaged, bent in tight turns or twisted. Using the motorcycle in this condition...
Inspect after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months afterwards. Caution! Throttle operation may be impaired when the throttle cables are damaged, bent in tight turns or twisted. Using the motorcycle in this condition...
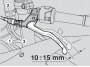
Throttle cable play adjustment
There should be 2-3 mm free play in the throttle twistgrip cable (measured at twistgrip edge). If not so: Place the motorcycle on the stand. Slip off the rubber gaiter (1). Loosen the locknut (2). Rotate the adjuster (3) until setting the specified...
There should be 2-3 mm free play in the throttle twistgrip cable (measured at twistgrip edge). If not so: Place the motorcycle on the stand. Slip off the rubber gaiter (1). Loosen the locknut (2). Rotate the adjuster (3) until setting the specified...
Idling adjustment
Adjust as follows whenever idling speed seems erratic. Ride a few kilometres until warming engine up to regular operating temperature. Place the gearbox in neutral. Look at engine idle speed (rpm) on the rev counter. Engine idling speed should be...
Adjust as follows whenever idling speed seems erratic. Ride a few kilometres until warming engine up to regular operating temperature. Place the gearbox in neutral. Look at engine idle speed (rpm) on the rev counter. Engine idling speed should be...
Cold-start cable play adjustment
There should be 2-3 mm free play in the cold-start cable. Play is adjusted as follows: Place the motorcycle on the stand. Lift the fuel tank; see 2.9.1. Adjust working from the left side of the motorcycle. NOTE. DO NOT disturb the rubber gaiter of...
There should be 2-3 mm free play in the cold-start cable. Play is adjusted as follows: Place the motorcycle on the stand. Lift the fuel tank; see 2.9.1. Adjust working from the left side of the motorcycle. NOTE. DO NOT disturb the rubber gaiter of...
Steering maintenance
Inspect after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months afterwards. The steering is fitted with rolling bearings to ensure smooth handling. Proper steering adjustment is vital to smooth steering movement and safe riding....
Inspect after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months afterwards. The steering is fitted with rolling bearings to ensure smooth handling. Proper steering adjustment is vital to smooth steering movement and safe riding....
Front suspension maintenance
The front suspension is managed by a hydraulic fork, which is held to the steering stem by two yokes. Note. Vehicle set-up may not be modified. Change front fork oil every 12,000 km (7456 mi). The following inspections should be performed every 8000...
The front suspension is managed by a hydraulic fork, which is held to the steering stem by two yokes. Note. Vehicle set-up may not be modified. Change front fork oil every 12,000 km (7456 mi). The following inspections should be performed every 8000...
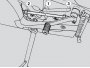
Rear swinging arm inspection
Periodically check that the nut-and-spindle assembly and the needle roller bearings of the swinging arm are properly tightened. Inspection procedure: Place the motorcycle on the front service stand (OPT); see 1.7.1. Remove the fuel tank; see 4.1.1....
Periodically check that the nut-and-spindle assembly and the needle roller bearings of the swinging arm are properly tightened. Inspection procedure: Place the motorcycle on the front service stand (OPT); see 1.7.1. Remove the fuel tank; see 4.1.1....
Rear suspension maintenance
Read 1.2.1 carefully. The rear suspension is managed by a spring/damper unit that is connected to the frame and to the rear swinging arm through silent-blocks and a linkage system, respectively. To modify vehicle response, the rear shock absorber is...
Read 1.2.1 carefully. The rear suspension is managed by a spring/damper unit that is connected to the frame and to the rear swinging arm through silent-blocks and a linkage system, respectively. To modify vehicle response, the rear shock absorber is...
Rear swinging arm adjustment
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Torque wrench settings: Spindle (1): 100 Nm (10.0 kg·m). Lockring (2): 35 Nm (3.5 kg·m). Lockring adjusting bush (3): 12 Nm (1.2 kg·m). Put the motorcycle on the front wheel stand (OPT), 1.7.1. Remove the fuel tank; see 4.1.1....
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Torque wrench settings: Spindle (1): 100 Nm (10.0 kg·m). Lockring (2): 35 Nm (3.5 kg·m). Lockring adjusting bush (3): 12 Nm (1.2 kg·m). Put the motorcycle on the front wheel stand (OPT), 1.7.1. Remove the fuel tank; see 4.1.1....
Inspecting the rear suspension linkage system
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Check bearings every 4000 km (2485 mi). Note. An assistant will be required to keep the vehicle upright during the procedure. Hold the tail of the motorcycle firmly with your hands. Press down and release repeatedly. If you...
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Check bearings every 4000 km (2485 mi). Note. An assistant will be required to keep the vehicle upright during the procedure. Hold the tail of the motorcycle firmly with your hands. Press down and release repeatedly. If you...
Wheels maintenance
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Front wheel Check every 4000 km (2485 mi). Place the vehicle on the front wheel stand; see 1.7.1. Rotate the wheel manually in both directions. The wheel should be spinning smoothly, with no hardness or unusual noise. If not...
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Front wheel Check every 4000 km (2485 mi). Place the vehicle on the front wheel stand; see 1.7.1. Rotate the wheel manually in both directions. The wheel should be spinning smoothly, with no hardness or unusual noise. If not...
Tyres maintenance
Check tyre condition after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2685 mi) or 8 months afterwards. It is a good rule to measure tyre inflation pressures before and after a long trip. Tyre inflation pressures should be checked monthly with the...
Check tyre condition after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2685 mi) or 8 months afterwards. It is a good rule to measure tyre inflation pressures before and after a long trip. Tyre inflation pressures should be checked monthly with the...
Exhaust manifold nuts
Tighten the exhaust manifold nuts after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months afterwards. Danger! Allow the engine to cool down to ambient temperature. Lift the fuel tank; see 2.9.1. Remove the battery mount; see 7.2.1....
Tighten the exhaust manifold nuts after the first 1000 km (621 mi) and every 4000 km (2485 mi) or 12 months afterwards. Danger! Allow the engine to cool down to ambient temperature. Lift the fuel tank; see 2.9.1. Remove the battery mount; see 7.2.1....
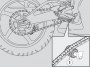
Drive chain maintenance
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Inspect and lubricate as required every 500 km (310 mi). This motorcycle is equipped with a master link chain. When dismantling and refitting the chain, be sure to install the master link clip (1) with the open end pointing...
Read 1.2.1 carefully. Inspect and lubricate as required every 500 km (310 mi). This motorcycle is equipped with a master link chain. When dismantling and refitting the chain, be sure to install the master link clip (1) with the open end pointing...
Chain slack inspection
To check chain slack: Stop the engine. Place the vehicle on the stand. Put the gearbox in neutral. Check chain slack in the lower straight portion of chain. The vertical movement of the chain midway between the sprockets should be approximately...
To check chain slack: Stop the engine. Place the vehicle on the stand. Put the gearbox in neutral. Check chain slack in the lower straight portion of chain. The vertical movement of the chain midway between the sprockets should be approximately...
Adjusting the drive chain
Torque wrench settings: Rear wheel spindle nut: 100 Nm (10.0 kg·m). If inspection proved the need for adjustment, set drive chain as follows: Position the vehicle on the rear wheel stand (OPT), 1.7.2. Completely loosen nut (1). Warning! For and...
Torque wrench settings: Rear wheel spindle nut: 100 Nm (10.0 kg·m). If inspection proved the need for adjustment, set drive chain as follows: Position the vehicle on the rear wheel stand (OPT), 1.7.2. Completely loosen nut (1). Warning! For and...
Checking chain and sprockets for wear
Visually inspect chain, front and rear sprockets looking for: Damaged chain rollers. Loose chain link pins. Dry, rusty, warped or seized links. Exceeding wear. Missing O-rings. Exceedingly worn or damaged sprocket teeth. Warning! If chain rollers...
Visually inspect chain, front and rear sprockets looking for: Damaged chain rollers. Loose chain link pins. Dry, rusty, warped or seized links. Exceeding wear. Missing O-rings. Exceedingly worn or damaged sprocket teeth. Warning! If chain rollers...
Chain cleaning and lubrication
Warning! Use the utmost care when adjusting, lubricating, washing or replacing the chain. Lubricate the chain every 500 km (310 mi) and whenever it seems appropriate. Lubricate with aerosol lubricant for chains or SAE 80W-90 oil. Never wash the...
Warning! Use the utmost care when adjusting, lubricating, washing or replacing the chain. Lubricate the chain every 500 km (310 mi) and whenever it seems appropriate. Lubricate with aerosol lubricant for chains or SAE 80W-90 oil. Never wash the...
Chain slider inspection
Place the vehicle on the stand. Check the chain slider (1) for damage or wear. Replace as required; see 7.1.15.
Place the vehicle on the stand. Check the chain slider (1) for damage or wear. Replace as required; see 7.1.15.
Similar subsections of other motorcycle models
Maintenance motorcycle Harley Street 750/500 (2014-2021)
Maintenance motorcycle Suzuki Boulevard M109R (2006-2025)
- Information for owner
- Introduction to manual
- Maintenance
- Troubleshooting
- Engine and systems
- Engine repair
- Fuel system
- Cooling and lube system
- Running gear and frame
- Frame and hinged elements
- Front suspension and handlebar
- Rear suspension
- Brake system
- Wheels and tires
- Electric equipment
- Equipment and devices
- Starting and charging system
Aprilia: RS-series Shiver (map) BMW: F-series R-series K-series (map) Ducati: ST series Monster (map) Harley: Street Sportster V-Rod (map) Honda: Africa Twin CB series VTX series (map) Kawasaki: ZX-6R Versys Vulcan (map) Suzuki: DR-Z V-Strom Boulevard (map) Triumph: Rocket Street Triple Tiger (map) Yamaha: Fazer DragStar R1 (map)